Urban areas worldwide face severe challenges – from congested traffic, and pollution to energy inefficiency and public safety. These issues intensify with an increase in the size of cities, thereby requiring some innovative solutions. The answer comes in the form of edge computing, a transformative technology empowering smart cities to take on the challenges of urbanization head-on. Let’s learn how edge computing is making cities smarter and more efficient while real-life success stories depict its effects.
Covered Contents
ToggleWhat is Edge Computing?
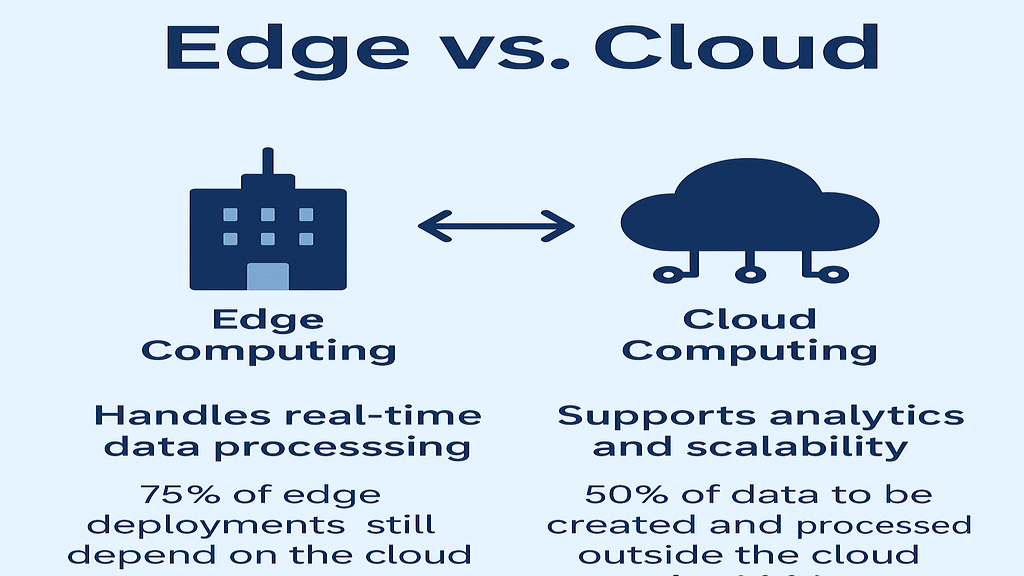
Edge computing is a decentralized kind of processing data, by performing calculations close to their sources—near the edges of a network. Such is contrary to traditional cloud computing methods that rely on far-flung data centers. Consequently, it accelerates data processes, lowers latency, and increases efficiency. Smart cities require this significantly, for they have data coming in real-time in volumes through IoT devices or sensors.
Urban Challenges Smoothened by Edge Computing
Traffic Regulation
Because it causes both environmental and economic harm, traffic congestion is a prevalent issue in cities. Edge computing enables adaptive signal management systems and real-time traffic monitoring.
For example:
Case Study: Barcelona, Spain
Barcelona uses edge-powered traffic management systems to examine real-time data from sensors and cameras. These systems change traffic signals in response to real-time data for dynamic adjustments, thus decongesting roads and easing travel times. Consequently, travel delays and emissions have dropped drastically in the city.
Public Safety
A smart city is always cautious about safety in crowded locations. Edge computing enables a more advanced surveillance system and the mechanisms of emergency response systems.
Case Study: Singapore
Singapore’s smart surveillance network uses edge computing to process video feeds locally. This gives real-time anomaly detection-identification of unauthorized access, for example, or recognition of suspicious activities. That means faster response times and safer public spaces.
Energy Efficiency
Cities use up enormous amounts of energy inefficiently. Edge computing has the potential to optimize energy consumption and incorporate renewable sources into the mix.
Case Study: Copenhagen, Denmark
Copenhagen employs edge computing to handle its smart grid management. Through real-time analytics of energy consumption patterns, the city can optimize distribution, reduce wastage, and seamlessly integrate renewable energy like wind and solar.
Waste Management
Effective waste management is the backbone of sustainability in cities. Edge computing enables data-driven waste collection plans.
Case Study: Seoul, South Korea
Seoul’s waste management system incorporates IoT-enabled smart bins equipped with edge computing capabilities. These bins monitor fill levels and notify collection teams in real-time, reducing unnecessary pickups and ensuring timely waste disposal.
Air Quality Monitoring
In metropolitan settings, air pollution poses major health concerns. Edge computing enables precise and immediate monitoring of air quality.
Case Study: Los Angeles, USA
Los Angeles uses edge-powered air quality sensors throughout the city. These sensors give real-time information on pollutant levels, which is useful for putting localized measures into place that effectively lower air pollution.
Benefits of Edge Computing in Smart Cities
Low Latency:
Decision-making is rapid with data processing at the edge level.
Improved Reliability:
Reduced dependence on centralized servers reduces downtime and loss of data.
Cost Efficiency:
Local processing of data decreases bandwidth utilization and cloud storage costs.
Scalability:
Edge solutions can easily scale to match the ever-increasing demands of developing cities.
Enhanced Security:
The processing of data locally limits the exposure extent to cyber-attacks and hence guarantees maximum privacy of data.
Conclusion
Edge computing is revolting urban management as cities become smarter, safer, and more sustainable. From optimizing traffic to air quality monitoring, edge computing has applications in that realm. As demand increases for smart city solutions, edge computing will continue to be the leading urban innovation area.
By learning from these success stories, cities all over the world can implement edge computing technologies to address unique challenges and make their lives brighter.


3 thoughts on “Edge Computing in Smart Cities”