Cloud computing and mobile computing are some phrases that nowadays are very widely used but, on closer inspection, refer to two quite different computing paradigms. Both have indeed changed how people access, store, and use data; but before opting for one, the major differences, benefits, drawbacks, and applications of each are to be understood.
The capacity to access computers, such as laptops, tablets, smartphones, and wearables, from any location without being confined to one area to access data and do tasks is known as mobile computing. Wi-Fi, 4G, 5G, Bluetooth, and portable devices are its main sources of power.
Cloud Computing
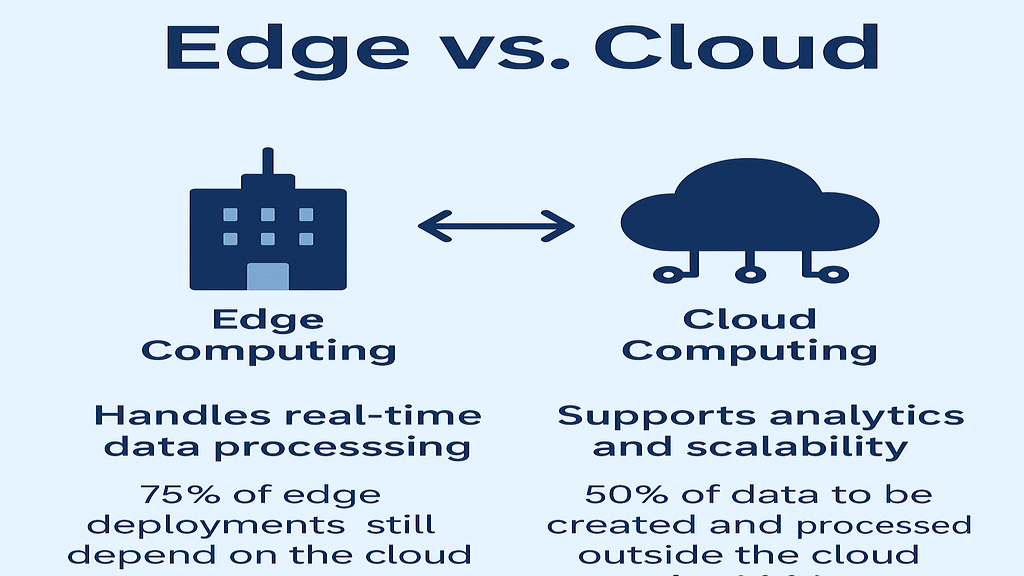
In contrast, cloud computing involves providing computing services, from servers and storage to databases and software and analytics over the Internet. Data centers are hosted remotely by the “cloud,” meaning the user can access any resource at will without ever having to maintain infrastructure in-house.
Covered Contents
ToggleImportant Features of Mobile Computing
Portability: Mobile devices are designed to be lightweight and portable, so working or communicating from almost any location is easy.
Access: With wireless connectivity, there is real-time access by using the device for navigation or social media, and there’s also work.
Convenience: Mobile computing removes dependency from static workstations and hence fosters productivity on the go.
Integration with sensors and GPS: Most mobile devices feature additional hardware such as cameras and GPS, and this serves to enhance user experience by enabling applications in health, travel, and gaming.
Important Features of Cloud Computing
Scalability: The scalability of cloud services makes it possible to increase or decrease according to demand. This gives flexibility to business entities of all sizes.
Cost efficiency: Cloud computing reduces initial investment in hardware and diminishes the cost of its maintenance.
Remote collaboration: Teams can collaborate smoothly with the help of access to shared data and applications anywhere in the world.
Data backup and recovery: Cloud provides automated backups and disaster recovery options that make sure critical information is saved.
Challenges of Mobile Computing
Battery Life:
Wireless devices are often plagued with short battery life, more so when used intensively.
Security Risks:
These devices are more vulnerable to stealing and unauthorized access, with security challenges.
Connectivity Dependence:
Mobile computing can be unreliable or very inefficient without stable network coverage.
Processing Power:
Such devices may lack the computing power needed for resource-heavy tasks compared to desktop computers or cloud-based solutions.
Challenges of Cloud Computing
Internet Dependency:
As such, cloud computing suffers significantly in areas far removed from the main connectivity infrastructure of this world.
Privacy for data:
Third-party server cloud storages of sensitive information invite much concern about privacy and compliance
System Failure:
Sometimes, cloud providers incur an outage, hence discombobulating business practices.
High-Cost Overruns:
Unless kept under control, mishandled cloud consumption invites unnecessarily high costs, even as firms scale up.
Usage Examples of Mobile Computing
Healthcare: Doctors and nurses use mobile devices for patient monitoring, accessing records, and real-time diagnostics.
Retail: Mobile point-of-sale (POS) systems streamline checkouts and enhance customer experiences.
Education: Mobile devices facilitate e-learning and virtual classrooms, providing flexibility to students and educators.
Travel and Navigation: GPS-enabled devices make it easier to navigate unfamiliar places or track real-time transport schedules.
Use Cases of Cloud Computing
E-Commerce: Cloud platforms host online stores, manage inventory, and process transactions efficiently.
Data analytics: Cloud computing enables businesses to comprehend vast volumes of data that could otherwise remain unanalyzed.
(SaaS): Software as a service (SaaS) is the service that enables users to access software straight from the cloud using apps like Microsoft Office 365, and Google Workspace.
Mobile Computing and Cloud Computing: A Collaborative
Future
Though mobile computing and cloud computing are distinct concepts, their integration is what’s going to define the future of technology. For example, more and more mobile applications require cloud services for storing data, synchronizing with multiple devices, and extending their capabilities. Such an integration brings out a smooth user experience where users can engage in real-time communication, work remotely, and have new applications like augmented reality and the Internet of Things.
Conclusion:
Mobile computing offers strong real-time accessibility and portability, and cloud computing provides scalability and central resource management.
The differences in the two systems lead to their respective advantages and challenges, which make them applicable to different contexts and applications. Understanding the roles they serve will enable businesses and users to utilize their strengths effectively to maximize productivity, deliver better user experiences, and innovate in the digital economy.
Whether you are using a smartphone on the move or using cloud-based services, these technologies are further redefining how we interact with the world around us.


One thought on “Mobile vs. Cloud Computing: Benefits, Challenges, and Applications”