Mobile Edge Computing is the revolution in how we interact with technology. It is a technology that brings computing power closer to users, hence improving speed and performance. The deployment models and operation of mobile edge computing will be covered in this post.
Mobile Edge Computing (MEC): What is it?
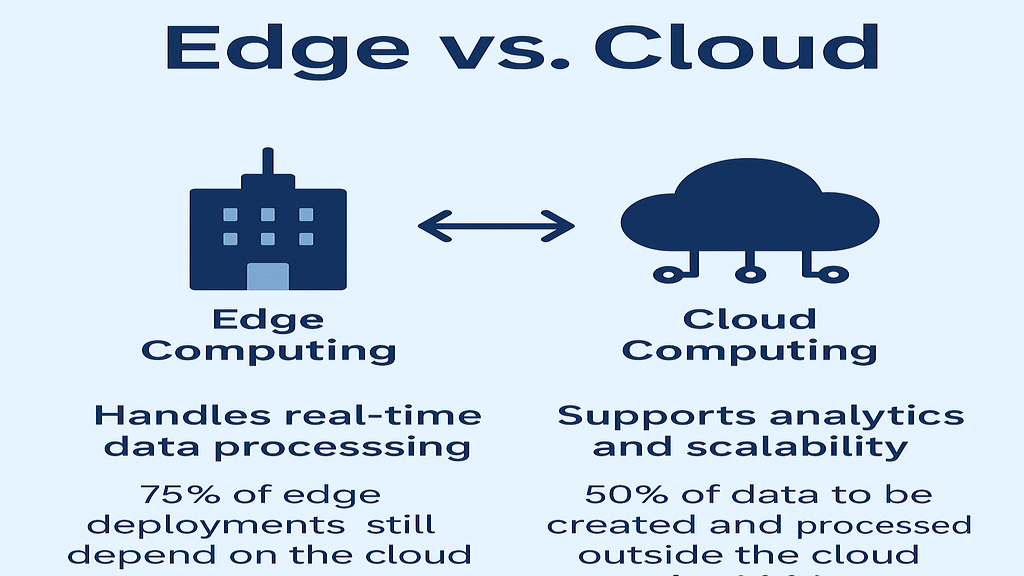
A technique called MEC brings computation closer to the network’s edge. This implies that MEC will allow devices to process data closer to the source rather than sending it to distant data centers.
Thus, latency is reduced as well as bandwidth, thus making services faster and more efficient.
The Two Main Deployment Models
There are two primary deployment models for MEC:
1.Centralized MEC
2.Decentralized MEC
Let’s look at each one in detail.
Centralized MEC Deployment
In centralized MEC, a central location, such as a large data center contains all the computing resources, and devices send their information to that central server, which then processes it.
-
Advantages of Centralized MEC
Easier Management: All resources management in one place is straightforward.
Cost-effective centralized systems can be established at a lower cost.
-
Disadvantages of Centralized MEC
Takes Longer Time: Since this data has to travel so far, it takes more time to process.
Bandwidth Use: Transferring vast amounts of data requires considerable bandwidth.
Decentralized MEC
Decentralized MEC has computing resources dispersed across the network. Such resources are closer to devices or at the edge of the network. The device is responsible for processing the data either locally or in nearby locations.
-
Advantages of Decentralized MEC:
Less Latency: Locality in processing leads to rapid response time.
Less Bandwidth Needed: Since less data needs to be sent to a central server, it saves bandwidth.
-
Disadvantages of Decentralized MEC:
Complex Management: Managing many small resources can be challenging.
Higher Costs: Setting up multiple locations can be more expensive.
Choosing the Right Model
The choice between centralized and decentralized models depends on the needs of the system.
If speed and low latency are crucial (like in the case of real-time games or autonomous vehicles), decentralized MEC is a better way.
If cost-efficient or easier management is concerned, then centralized MEC is to be used.
Hybrid Approach
Hybrid models use the advantage of both centralized and decentralized system models. Some tasks, or even some data processing, happen at the central level, but other tasks and data processing occur at the edge or near the source. With this model, efficient management, cost-cutting, and better control can be accomplished while latency and bandwidth use are minimized due to on-demand processing at local levels of data. The hybrid approach is very useful in complex systems where different tasks have varying requirements for speed, cost, and control, offering a balanced solution adapted to specific needs.
Conclusion
The mobile edge computing deployment model has been identified to significantly influence the improvement of mobile services. Centralized MEC has easy management, and is less costly, and its decentralized counterpart offers speed and performance. The knowledge about such models is helpful when a business has to determine what model to use based on their specific needs.
It helps businesses choose the right deployment model that enhances user experience and reduces delays efficiently.

One thought on “Mobile Edge Computing Deployment Models: A Simple Guide”