Technology is pervasive in today’s fast-paced technological environment. We are surrounded by devices that are always gathering, sending, and evaluating data. Every second, enormous volumes of data are produced by wearables, smartphones, smart homes, and industrial machinery. However, how can we effectively handle this data in real time?
Edge computing comes into play here. Rather than depending on distant data centers or the cloud, it processes data locally. The way we handle information is changing as a result of this innovative technology. We’ll examine edge computing, operation, and growing importance in our technologically advanced society in this guide.
Covered Contents
ToggleWhat is Edge Computing?
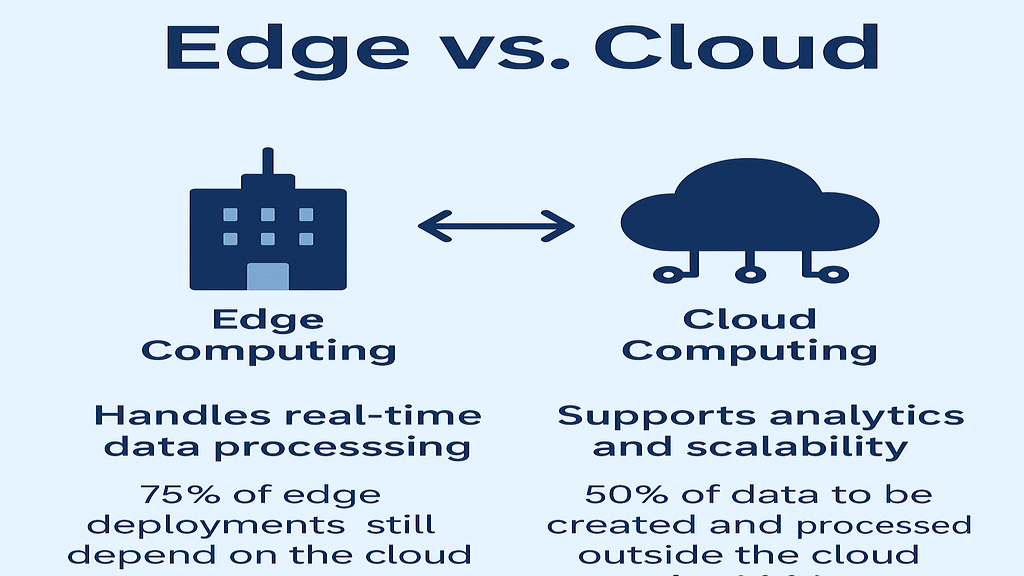
Edge computing is a distributed computing platform that brings processing and data storage closer to data sources. Unlike traditional systems that transport all data to central servers or the cloud, edge computing processes information locally on devices or adjacent network nodes.
Consider edge computing as the placement of little data centers next to devices that generate data. Faster decision-making, less reliance on the cloud, and less network congestion are all made possible by this configuration.
Why is Edge Computing Important?
In the modern world, equipment from many different businesses produce enormous volumes of data. For example, sensors in self-driving cars gather data on traffic, road dangers, and vehicle status in real time. Delays may result from sending this data to cloud servers for processing, which could cause mishaps. By analyzing data inside the car, edge computing addresses this issue, facilitating quick decisions and improving safety.
There are several key reasons why edge computing is becoming critical:
Low Latency:
With edge computing, data doesn’t need to travel long distances to reach a central server. This reduces the delay, making systems more responsive, especially in real-time applications.
Bandwidth Efficiency:
By processing data locally, edge computing reduces the need to send large volumes of data over networks, saving bandwidth and lowering costs.
Improved Security:
Because it processes data on the local side, it doesn’t need to transmit it to any external servers that might pose a danger of hacking and improve privacy.
Reliability:
Edge computing ensures that even if there’s a disruption in network connectivity, the local system will be able to function autonomously without affecting any cloud dependencies.
How Does Edge Computing Work?
Edge computing works by using local devices, computing resources, and network infrastructure but processing data closer to its origin. Here is a simple breakdown:
Data Generation:
The first step towards edge computing is data generation. In this process, some devices such as sensors, cameras, or wearable devices, generate and transmit data.
Local Processing:
Rather than that, edge computing facilitates processing this data on devices, gateways, or micro-data centers placed nearby instead of sending them to the cloud.
Decision making:
Once the data has been processed edge computing systems can make decisions on edge applications immediately based on the processed data. For instance, smart manufacturing machines detect faults, therefore immediately stopping before facing breakdowns without waiting for a response from a cloud server.
Data Transfer:
Though most of the data would be processed at the edge, there could still be instances of sending that data to the cloud for further processing, storage, or even long-term decisions. In that case, it is done in a much more streamlined and efficient way.
Key Advantages of Edge Computing
Edge computing has emerged as a game-changer for many industries. Here are some of the key advantages:
-Speed and Low Latency
For instance, for applications such as autonomous driving or real-time industrial monitoring, even a slight delay can be catastrophic. Edge computing processes data on the spot, thus minimizing latency and providing rapid responses. For instance, in the case of autonomous vehicles, decisions to avoid collisions must be made in split seconds. Edge computing ensures that decisions are made immediately, rather than waiting for data to travel to the cloud.
-Cost Savings:
The cost of data transmission would be saved as the processing of data occurs locally. For instance, devices in a smart city that produce huge amounts of data, such as traffic cameras or environmental sensors, need not send all the data to the cloud for processing; only necessary data is transferred to the cloud, thus decreasing bandwidth usage and cloud storage cost.
-Better Security and Privacy
With edge computing, sensitive data is processed locally, and data breaches or hacking while in transit are relatively less possible. In cases like the health sector, healthcare information remains inconspicuously private and secure. For example, a health monitoring device can evaluate a user’s statistics directly on the device instead of transmitting individual data to external servers.
-Reliability in Remote Areas
In places with no internet connection, edge computing is critical. Areas with limited internet access include remote farms, oil rigs, and remote military bases, which process data on their devices locally. Even when they lose connection, the devices can function autonomously.
Applications of Edge Computing in Different Industries
Edge computing is revolutionizing many sectors by enabling faster, smarter, and more efficient systems. Edge computing is now being applied across industries in the following ways:
Autonomous Vehicles:
Edge computing enables autonomous vehicles to make decisions within split seconds. In autonomous vehicles, edge computing processes real-time sensor data from cameras, radar, and LiDAR to ensure split-second decisions are made regarding the detection of obstacles, lane changing, or speed changes, all of which need to occur with minimal latency.
Healthcare:
In healthcare, edge computing is used in devices such as wearable fitness trackers, remote patient monitoring, and even medical imaging. Devices that monitor heart rates, blood oxygen levels, or ECG readings can process data locally to detect irregularities and send alerts without waiting for cloud processing.
Check it:
What Are the Benefits of Using Wearable IoT Technology?
Smart Cities:
Edge computing further helps process all the data coming from different sensors in smart cities, such as cameras monitoring traffic, environmental sensors, and smart meters. All this processed data could be used to best optimize traffic flow and monitor air quality and efficiency in using energy without vast transfers of data to a central system.
Industrial IoT (IoT):
In industrial settings, edge computing is used for predictive maintenance by monitoring machines and equipment. Here, the local sensors capture data about machine performance, which edge computing analyzes to predict when a machine might fail, thereby allowing operators to intervene before a breakdown.
Check it:
The Future of IoT: Transforming Everyday Life with Smart Devices
Retail and Customer Experience:
Edge computing helps retailers offer personalized recommendations, efficient inventory management, and cashierless checkout systems.
For example, facial recognition can analyze data of customers locally for personally related services and promotions.
Challenges and Considerations with Edge Computing
Of course, with its numerous benefits comes its set of challenges and considerations with edge computing.
Complexity:
Edge computing solutions can be complex because they require significant amounts of infrastructure, especially in large-scale environments, such as factories or smart cities.
Data Synchronization:
Because data will be processed locally, it can become challenging to sync and analyze data from multiple edge devices. Seamless intercommunication among devices and the cloud can ensure effective operations.
Advantages in Security:
Edge computing strengthens security in some cases but opens up new avenues of attack. Proper securing of edge devices from unauthorized access and tampering prevents new modes of attacks.
Resource Constraints:
Edge devices usually have more processing capabilities and storage than cloud data centers. They must, therefore, be optimized for specific tasks without overloading.
The Future of Edge Computing
The future of edge computing looks incredibly promising. As more devices and applications demand real-time processing, edge computing will continue to grow in importance. Advances in 5G technology, which will enable faster and more reliable connections between devices, will further accelerate the adoption of edge computing in industries like manufacturing, healthcare, and transportation.
Additionally, edge computing will increasingly be used with other new technologies, such as AI and machine learning, to ensure that the resulting systems will be much more intelligent and efficient. As we are moving into a much more interconnected world, edge computing will play an important role in ensuring fast, secure, and efficient processing of data at the source.
Key Points:
Edge computing is changing the methodology of handling data in the digital world. Edge computing offers faster processing speeds, improved security, and cost savings as processing is now done locally at the “edge” of the network. It plays an important role in various industries, such as autonomous vehicles, smart cities, and healthcare applications, which require the processing of real-time data. While the world continues to crave and demand a better, faster, and more efficient system, edge computing holds a place for future technology.
Learn More:
What Is Edge AI? How It Works, Types, and Applications


18 thoughts on “Edge Computing: A Simple Guide for Beginners”