Today, in this world, faster and more reliable services for the likes of IoT (Internet of Things), 5G, and autonomous vehicles demand new computing models. Edge computing is one of the most important developments of the distributed computing framework to bring data processing closer to the source of data.But what is the key enabler of edge computing? The answer lies in data centers—the foundation of edge computing networks.
Covered Contents
ToggleWhat is Edge Computing?
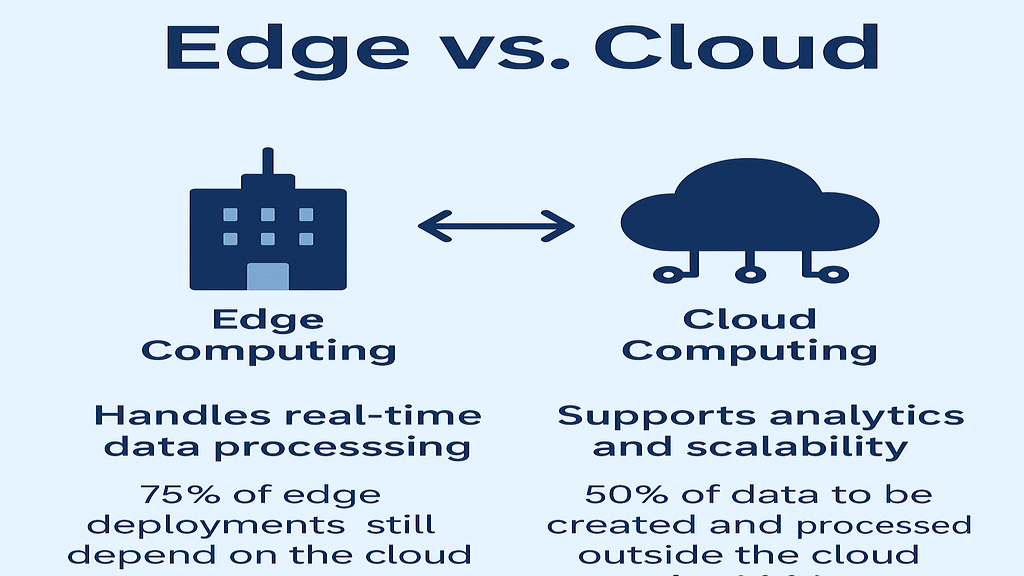
Edge computing is a decentralized computing model that strives to process the data nearer to the machines and the users that originated it instead of relying on distantly centralized data centers. This model reduces latency, optimizes bandwidth, and cuts down on response times – all these are crucial characteristics for applications that require operations in real-time, especially autonomous vehicles, industrial automation, and content delivery networks.
The core concept of edge computing is to process as much computing as possible at the “edge” of the network from which the data originates. It can reduce dependency on large data packets and cloud central servers that cause latency. Thus, an edge computing network is well-equipped to enhance performance while offering faster and more efficient service to the users.
The Role of Data Centers in Edge Computing Networks
Data centers, on the other hand, have proven to be the backbone of not only cloud computing but also of edge computing networks.It is the place where edge computing is supported by holding the hardware and infrastructure that provide the physical and virtualized resources required for local data processing. Now, let’s see in detail why data centers play a crucial role in the edge computing system:
Data Processing at the Edge
Although edge computing relies on processing data closer to the source, there is still a need for centralized infrastructure for storage, power, and backup processing. Data centers provide this support by housing edge computing nodes, micro data centers, and servers that handle local computations.In many edge computing setups, the data centers are regional hubs where data can be processed before it is forwarded to the cloud for more extensive analysis.
For example, in a smart city, traffic sensors would collect real-time data which is processed locally in an adjacent data center to adjust the traffic signals or allow quick response times for emergencies. These data centers enable computation and storage locally so that actual decisions can be made instantaneously without delay.
Scalability and Flexibility
Edge computing networks have to be highly scalable, as they may include thousands of devices such as sensors, cameras, or autonomous vehicles spread across large geographic areas. Data centers are the backbone by providing infrastructure that can easily scale up with growing data traffic and the processing requirements of edge computing applications.
Flexibility:
computing power, storage, network connectivity. Data centers can easily support edge computing services in rapidly changing environments since they can scale up or down as needed and make sure that the network grows alongside new technologies and more devices.
Latency Reduction and Increasing Speed
Reducing the latency involved in data transmission to and from distant data centers is one of edge computing’s primary benefits. To put it simply, edge computing reduces the distance that data must travel and speeds up reaction times by bringing the computer resources nearer to the data source.
Data centers are deliberately situated at the edge of networks to improve this performance.
For instance, data centers might be placed closer to mobile towers, 5G base stations, or urban areas where there is a high concentration of users. By distributing computing power across several smaller, localized data centers, edge computing reduces the reliance on a single centralized cloud, cutting down on latency and enhancing overall system speed.
Data Storage and Security:
Edge computing generates data, as well as processes, on a number of endpoints and devices. This kind of decentralized model is excellent in its own right, but it does bring significant data security and storage concerns. Data centers provide a secure, controlled environment in which sensitive data can be transmitted to be stored before further processing is done in the cloud or other systems.
Data centers for edge computing networks provide local storage options that keep important data near the source while still being available for backup and analysis, thereby reducing the risk of data loss and providing additional security through advanced encryption, access control, and compliance standards.
Why Data Centers are Critical for Edge Computing Success
This has introduced some benefits to industries that require real-time data processes:
Data center integration in networks increases efficiency, as centrally hosted data centers are spared more burden and resources when making use of bandwidth at such places.
Response rate also increases because the place for processing data is situated next to the source- Edge Computing minimizes latency found within cloud-based systems:
Cost-Effectiveness: Edge computing reduces the need for extensive data processing in the cloud, a factor that can save many businesses money on network bandwidth and storage.
Reliability: Data centers provide redundancy and backup systems, hence ensuring that edge computing networks can operate smoothly even with a failure or outage
Conclusion
This edge-computing paradigm shift has emerged at a time when the demand for fast, efficient data processing continues to grow. Data centers lie at the heart of this paradigm shift, playing the critical role of a foundational element for edge computing networks. With the necessary infrastructure, scalability, and security to support distributed data processing, data centers enable seamless operations of edge computing technologies that power industries such as IoT, 5G, autonomous vehicles, and much more.
With real-time data processing gaining importance, the role of data centers in supporting edge computing is not one to be underrated. They are the keys to making sure that the edge networks are functional, fast, secure, and scalable enough to make way for innovations that will shape the future of technology.

3 thoughts on “Data Centers: The Foundation of Edge Computing Networks”