Covered Contents
ToggleINTRODUCTION
Intelligent, quicker, and more secure data-handling techniques are desperately needed as the Internet of Things (IoT) and the proliferation of linked devices grow. The modern network’s workhorses are edge gateways. These products transform data processing, analysis, and security by acting as interfaces between the cloud and IoT sensors, industrial machinery, or smart devices. This article will explain edge gateways, including their definition, operation, advantages, and practical uses.
What Is an Edge Gateway?
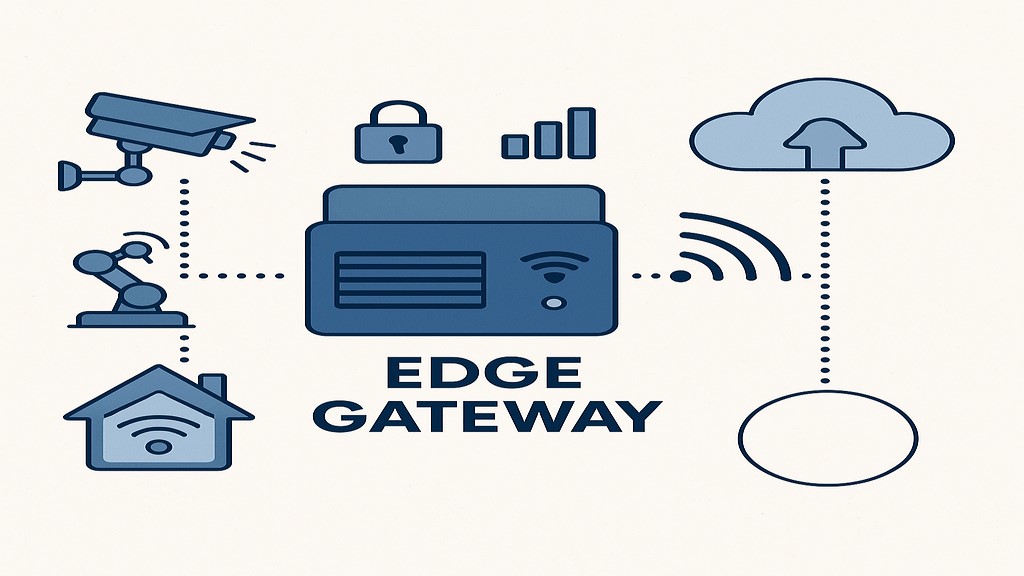
An edge gateway is a piece of hardware or software that is positioned close to IoT devices, sensors, or machinery at the “edge” of a network. Its primary function is to collect, process, and filter data locally before sending the most relevant information to central servers or the cloud. Consider a modest data center that avoids reliance on distant cloud services while carrying out important tasks on-site.
Key Functions of Edge Gateways
-Protocol Translation: Bluetooth, MQTT, Modbus, and other alternative protocols are commonly used by IoT devices to interact. Edge gateways convert these into common forms (like HTTP) so that cloud integration is simple.
-Data Analytics & Processing: Before sending a smaller amount of data to the cloud, they first filter, aggregate, and analyze the data locally. For example, instead of continuously streaming video, a security camera might play a video of something questionable.
-Security Enforcement: Edge gateways authenticate devices, encrypt traffic, and block unauthorized access. Cyber dangers are prevented by technologies like Trusted Platform Modules (TPM) and secure boot.
-Connectivity management: Wi-Fi, 5G, Ethernet, and other multivariate interfaces are made possible by connectivity management, which also ensures dependable connections in challenging conditions.
-Offline Operation: Edge gateways continue to process and store data locally in the event of a network interruption, ensuring system dependability.
Why Edge Gateways Matter: 5 Key Benefits
1. Reduced Latency for Decisions Made in Real Time
When data is sent to distant cloud servers, edge gateways minimize the latency (waiting period). For applications like driverless cars, where millisecond choices prevent collisions, this is crucial.
2. Savings on Storage and Bandwidth
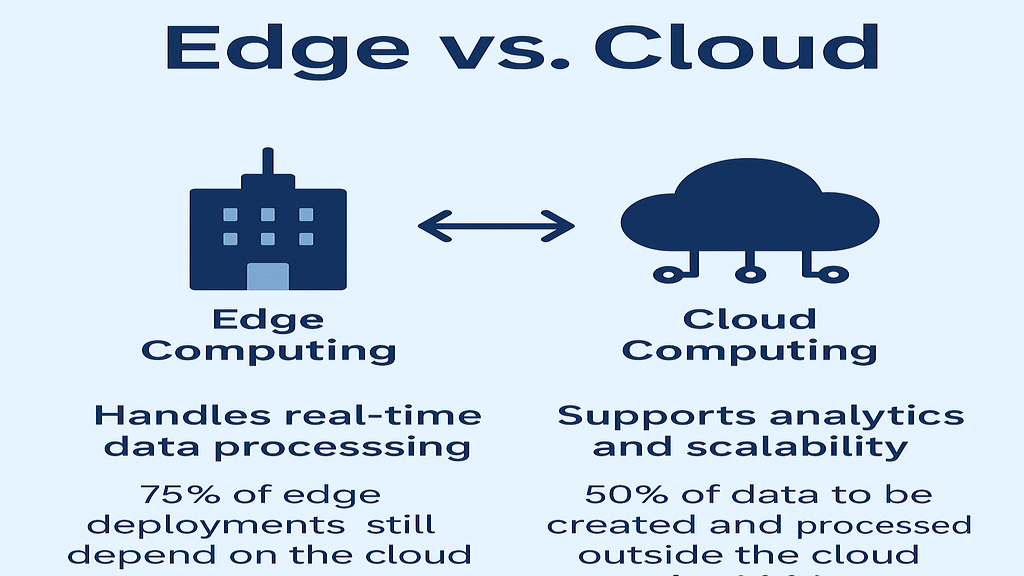
It is expensive to send unprocessed data from hundreds of devices to the cloud. By removing superfluous data, edge gateways can cut down on cloud storage and bandwidth utilization by up to 95%.
3. Improved Privacy & Security
Data processing locally lowers the risk of cyberattacks during transmission. Medical gadgets, for instance, can process patient data locally, reducing the possibility of sensitive data being intercepted.
4. Scalability for Network Expansion
Modular edge gateways (such as Compulab’s hardware, which can be customized) enable companies to introduce new devices or protocols without replacing their infrastructure.
5. Endurance in Adverse Situations
Industrial-grade edge gateways are made to bear harsh conditions like dust, shock, and temperature. They enable continuous operation in oil platforms, factories, and smart cities.
Edge Gateway Use Cases: Where They Shine
1. Intelligent Transportation & Networked Automobiles
Sensor data, traffic light data, and road camera data are all gathered via automotive edge gateways. They process this locally to optimize route-spread, alert drivers to hazards, and potentially facilitate autonomous driving. They also prevent attempts at vehicular network hacking by pre-filtering data before transmitting it to the cloud.
Learn more:
Edge computing: Role in autonomous vehicles
2. IoT for Industry (IIoT)
Edge gateways are used by factories to incorporate outdated machinery into modern IoT systems. For example, AI-based quality inspectors can be integrated with an existing conveyor belt that is thirty years old. The gateway minimizes downtime and enables predictive maintenance by converting outdated protocols (like RS-485) into modern standards.
3. Smart Cities
Edge gateways process real-time data from sensors for air quality and traffic lights to improve the intelligence of urban systems. In Barcelona, Spain, edge-powered smart streetlights adjust their brightness according to foot traffic, saving energy and improving safety.
4. Medical Surveillance
Hospitals employ edge gateways to assess patient vitals from wearable devices. Instead of waiting for cloud processing, the gateway provides a local alarm when a patient’s heart rate spikes sharply 58.
5. Supply Chain & Retail
Stores use edge gateways to analyze consumer behavior from intelligent shelves and track inventory using RFID tags. Following safety regulations, supply chains monitor temperature-sensitive goods (such vaccinations) in real time.
6. Monitoring of Agriculture and the Environment
Farmers utilize edge gateways to gather information from irrigation systems, weather stations, and soil sensors. Without ongoing cloud connectivity, this information forecasts crop yields, maximizes water usage, and identifies pests.
Learn more:
Edge AI in Offline Processing for Low-Connectivity Regions
The Future of Edge Gateways
1. The Edge of AI
AI-enabled hubs are emerging from edge gateways. Tuya’s Edge Gateway, for example, supports Docker containers to host machine learning models locally, enabling real-time analytics for equipment failure prediction or fraud detection.
2. Edge Networks Powered by 5G
5G’s extremely low latency will allow edge gateways to process data more quickly than in the past. This will open up new uses, such real-time drone monitoring or augmented reality (AR) for remote factory repairs.
3. Cloud-Edge Convergence
Cloud scale and on-premises processing are combined in solutions like Lumen’s Edge Gateway. Businesses can save money on hardware by virtualizing network functionalities (such as firewalls and SD-WAN) onto a single device.
4. Sustainability Focus
By limiting data transmission, edge gateways save energy. Smart grids, for example, employ them to balance electricity usage locally, reducing dependence on fossil-fuel-based data centers.
Selecting the Right Edge Gateway
In choosing an edge gateway, think about
Connectivity Options: Does it support earlier industrial protocols, 5G, or Wi-Fi as connectivity options?
Durability: Does it have a vibration or extreme temperature rating?
Features of Security: Verify encryption, secure boot, and TPM.
Scalability: Can you update your program or add new modules as needed?
Businesses like Compulab and Tuya offer robust, adaptable solutions that are ideal for sectors like manufacturing and healthcare.
Conclusion
The IoT revolution is rooted in edge gateways, which provide fast decisions, reduced costs, and strong security. Their uses are numerous, from energizing industries to protecting autonomous vehicles. The devices will become increasingly intelligent as 5G and AI continue to evolve, further closing the gap between the physical and digital worlds. Edge gateways are the solutions to the complete potential of connected technology, be it constructing a smart city or enhancing a retail shop.

2 thoughts on “What Are Edge Gateways? Functions, Benefits, and Use Cases Explained”